
Adding A Local Project to an Empty Github Repository The main argument represents the new default branch name (updated from master in most cases.) This will avoid pushing a second master branch to new empty Github repos with an empty main default branch. To reconfigure one’s local GIT software’s default branch name use the following command: GIT may not reflect this change when creating local projects first. A previous version of this article described pushing things to master but has been updated to reflect the change. git initĢ022 Update: Github has changed the name of the default branch from master to main. Note: this will delete anything currently in the remote repo.
#Git add remote and init code
The following code will ensure your local project makes it to the remote repo every time. TL DR – Github’s instructions for adding a local project to an empty repo don’t always work out as expected. Unfortunately, the instructions offered by Github on an empty repo’s URL don’t always work out smoothly. This is a useful workflow for local projects in need of remote versioning.

> destination FORKER/REPOSITORY.Adding a local project to an empty repository on Github is an easy process. > destination FORKER/REPOSITORY.git (fetch) It does not delete the remote repository. Removing the remote URL from your repository only unlinks the local and remote repositories.
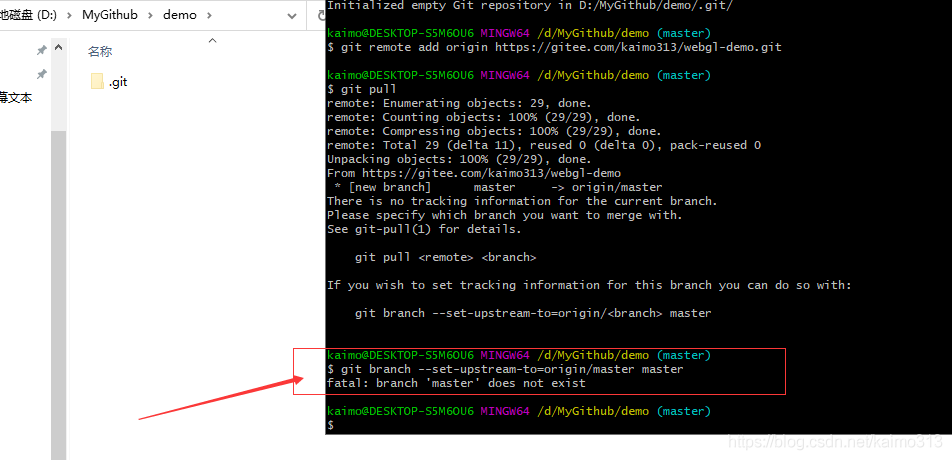
Use the git remote rm command to remove a remote URL from your repository. To solve this, either use a different remote name, or rename the original remote. This error means that the remote name you want to use already exists. > origin OWNER/ REPOSITORY.git (push) Troubleshooting: Remote already exists You can check which remotes currently exist with the git remote -v command: $ git remote -v This error means that the old remote name you typed doesn't exist. > destination OWNER/ REPOSITORY.git (push) Troubleshooting: Could not rename config section 'remote.' to 'remote.' > destination OWNER/ REPOSITORY.git (fetch) # Change remote name from 'origin' to 'destination' These examples assume you're cloning using HTTPS, which is recommended. A new name for the remote, for example, destination.An existing remote name, for example, origin.The git remote rename command takes two arguments: Use the git remote rename command to rename an existing remote. This error means that the remote you tried to change doesn't exist: $ git remote set-url sofake Ĭheck that you've correctly typed the remote name. Change your remote's URL from HTTPS to SSH with the git remote set-url command.You can use a credential helper so Git will remember your GitHub username and personal access token every time it talks to GitHub. For more information, see " Creating a personal access token." Password-based authentication for Git has been removed in favor of more secure authentication methods. Alternatively, you can use a credential helper like Git Credential Manager. When Git prompts you for your password, enter your personal access token (PAT). The next time you git fetch, git pull, or git push to the remote repository, you'll be asked for your GitHub username and password. Verify that the remote URL has changed.$ git remote set-url origin USERNAME/ REPOSITORY.git Change your remote's URL from SSH to HTTPS with the git remote set-url command.List your existing remotes in order to get the name of the remote you want to change.Change the current working directory to your local project.If you're updating to use SSH, your URL might look USERNAME/ REPOSITORY.git.If you're updating to use HTTPS, your URL might look like:.For example, origin or upstream are two common choices. The git remote set-url command takes two arguments: Tip: For information on the difference between HTTPS and SSH URLs, see " About remote repositories." The git remote set-url command changes an existing remote repository URL. For more information, see " Removing a remote repository" below. Delete the existing remote repository before you add the new remote.For more information, see " Renaming a remote repository" below. Rename the existing remote repository before you add the new remote.
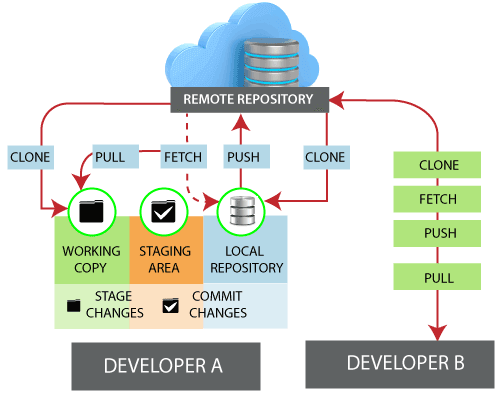
Use a different name for the new remote.This error means you've tried to add a remote with a name that already exists in your local repository. The git remote add command takes two arguments:įor example: $ git remote add origin user/ repo.gitįor more information on which URL to use, see " About remote repositories." Troubleshooting: Remote origin already exists To add a new remote, use the git remote add command on the terminal, in the directory your repository is stored at.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
